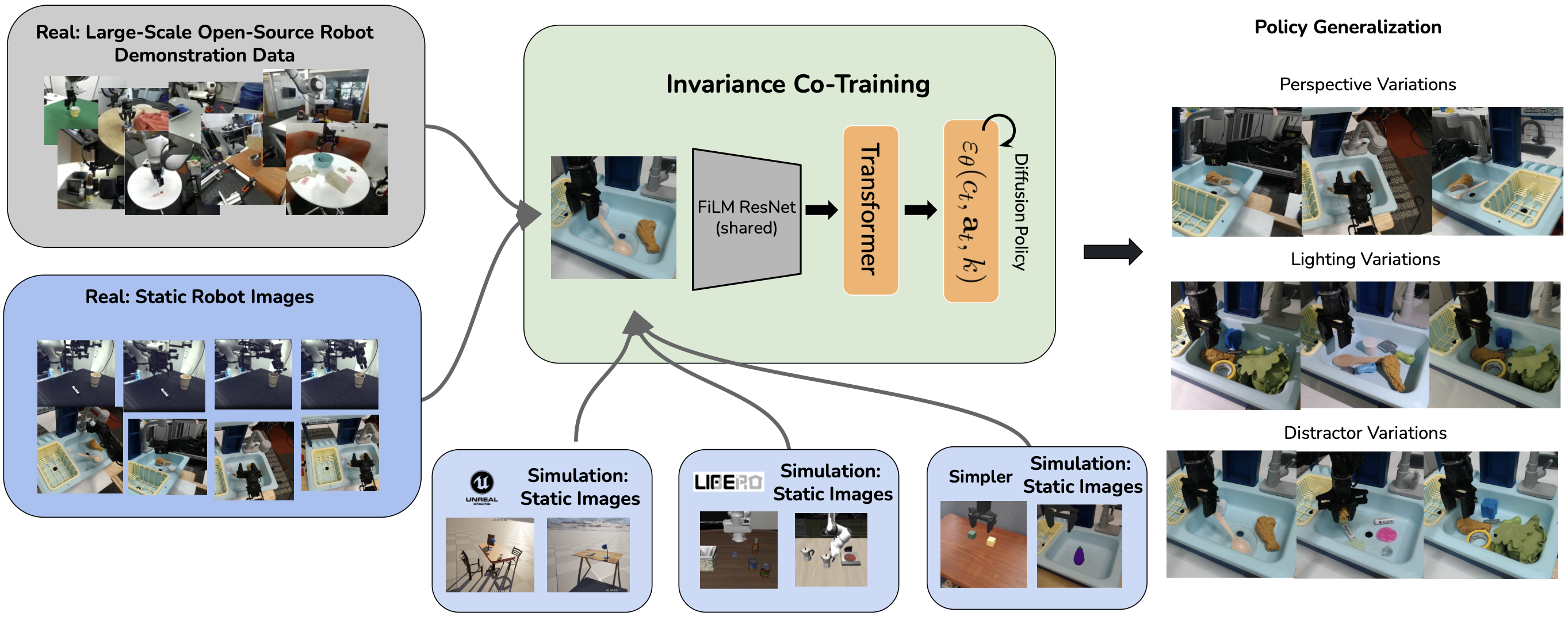
Despite recent advancements, many large-scale robotic policies still remain sensitive to key sources of observational variation—such as changes in camera perspective, lighting, and the presence of distractor objects. We posit that the limited generalizability of these models arises from the substantial diversity required to robustly cover these quasistatic axes, coupled with the current scarcity of large-scale robotic datasets that exhibit rich variation across them.
In this work, we propose to systematically examine what robots need to generalize across these challenging axes by introducing two key auxiliary tasks—state similarity and invariance to observational perturbations—applied to both demonstration data and static visual data. We then show that via these auxiliary tasks, leveraging both more-expensive robotic demonstration data and less-expensive, visually rich synthetic images generated from non-physics-based simulation (e.g., Unreal Engine) can lead to substantial increases in generalization to unseen camera viewpoints, lighting configurations, and distractor conditions.
Our results demonstrate that co-training on this diverse data improves performance by 18% over existing generative augmentation methods.
We propose a contrastive co-training framework where the policy learns representations invariant to observational perturbations (e.g., viewpoint, lighting) while remaining sensitive to task-relevant state and goal changes. By distinguishing between semantically similar and dissimilar (state, goal) pairs across varying observational conditions, the model learns to align representations that matter for control.

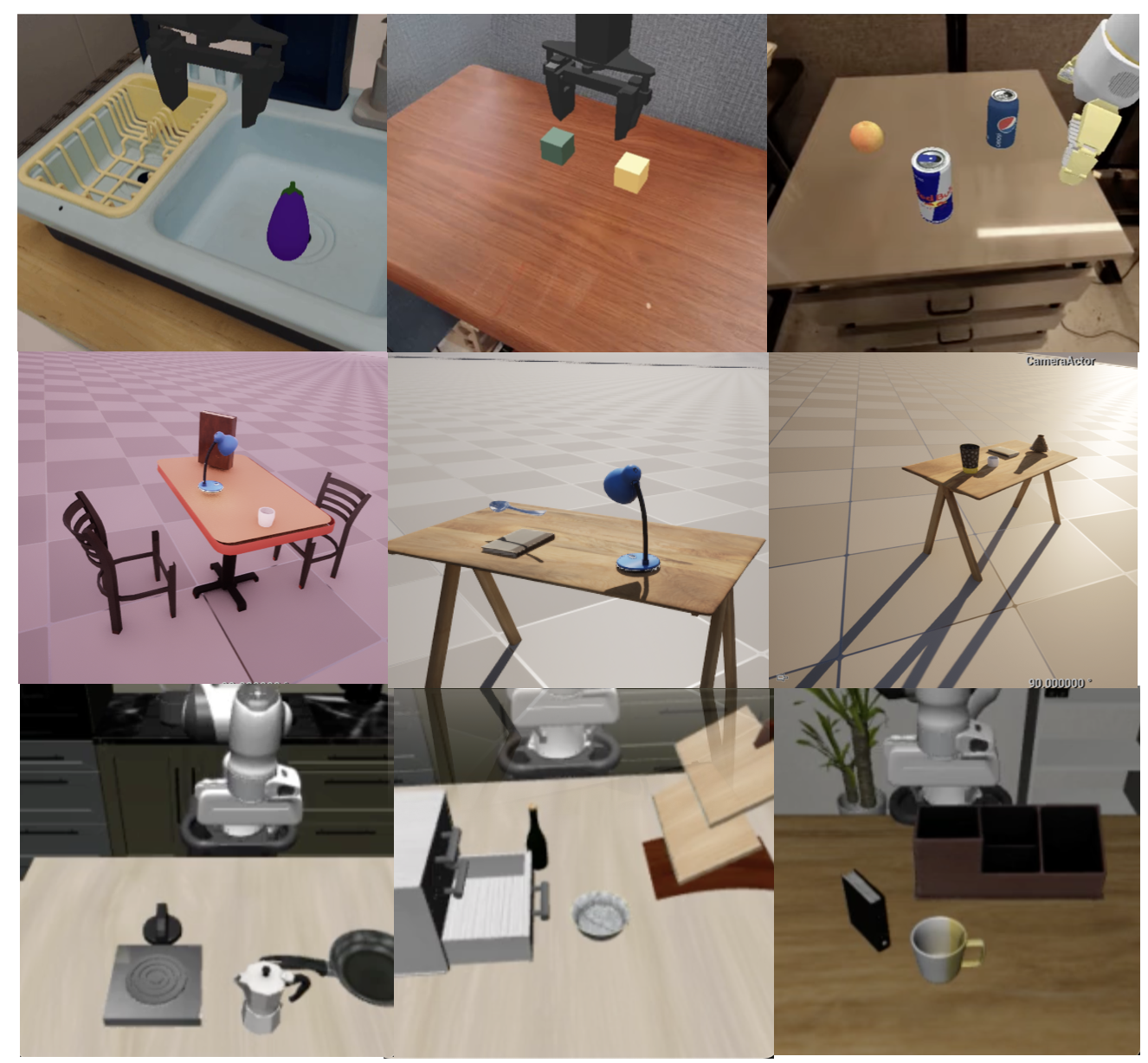
The image depicts example simulation images from the simpler env, unreal engine, and libero simulators.

Experimentally, our invariance co-training approach significantly outperforms baseline Behavioral Cloning, improving average success rates by approximately 40% across key variations. Furthermore, it yields 18\% higher success rates compared to variants relying only on simulation or generative models.
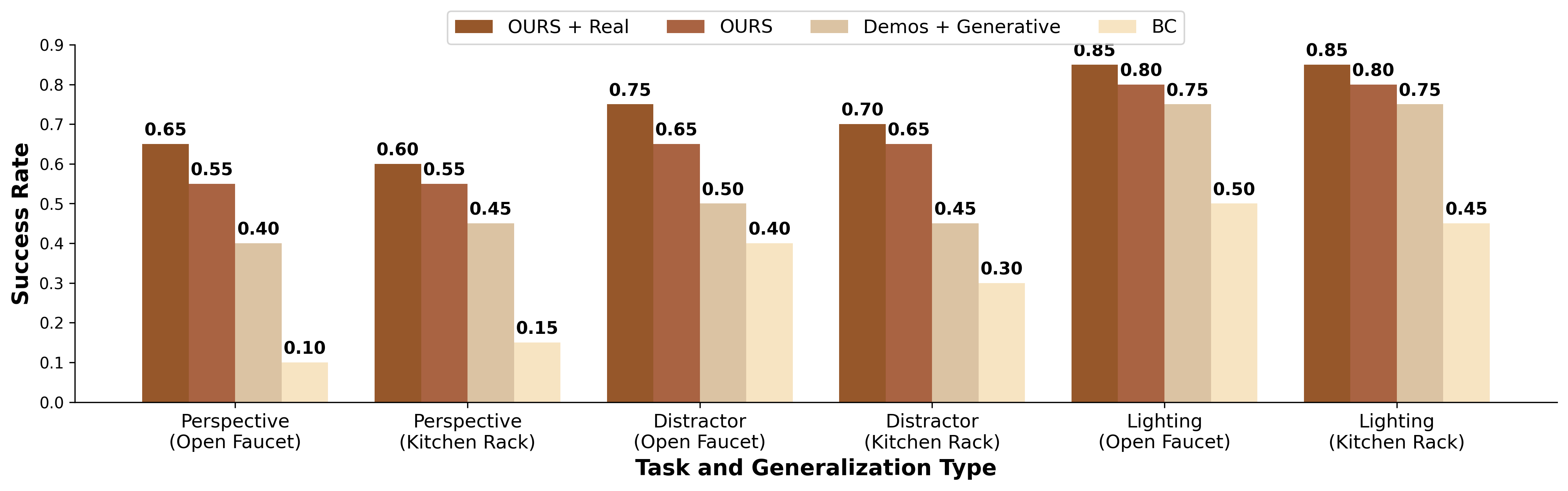
Quantitative Results: Our Invariance Co-Training approach consistently outperforms baseline methods across camera viewpoint changes, lighting variations, and background clutter scenarios.



Baseline Behavior Cloning struggles with viewpoint changes, background clutter, and lighting variations


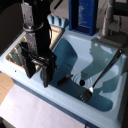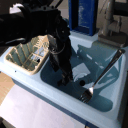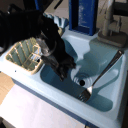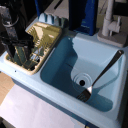
Our Invariance Co-Training approach successfully handles the same challenging variations
Our method can generalize to new camera perspectives zero-shot in the DROID platform.